Well, friends, this is one of those “is it just me?” confessions where I admit that for years I’ve been saving my research bibliographies and PDF versions of scholarly articles in a variety of folders on 3 different computers and with a filename system that has been… inconsistent at best. It hasn’t hindered me too much, but it’s bothered me, knowing there had to be a better way, and preferably an open-source, cloud-syncing and web-friendly way.
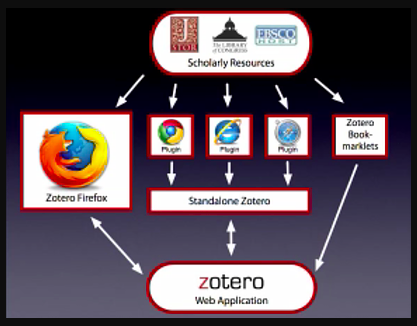
Image from Lidia Levkovitch’s helpful blog post “A Grad Student’s Guide to Zotero“
For me, that’s been Zotero. You can make a free account here, download the standalone application for your laptop or desktop computer here (mobile is not quite as stable, in my experience so far at least), download the plug-in for your favorite browser here (it seems to play especially well with Chrome for me), and — if you’re interested — see my current research project public folders here. It has been good for me to think about the taxonomy of my sources, what belongs with what, and why. Here are a few of my favorite things about it:
-
Zotero keeps research organized. No more folders of random files saved with names and dates. What a relief!
-
For articles and book chapters, it can save the actual PDF files for you, even with your annotations, and has a cool shortcut to rename files consistently for you so you aren’t stuck with the opaque name like 0986543.pdf that EBSCO decided to give you.
-
You can easily share your working bibliography, including the constituent folders, with others when collaborating by making a “group” – even if you’re the only member in your group!
-
It can handle a huge range of genres of sources: books, articles, websites, multimedia files, and just about anything else you can come up with to want to save.
-
You can save a source in more than one collection (folder) — so in my case, if an article has to do with both narrative theory AND Victorian women’s periodicals (be calm my heart!) with a simple click and drag, I can assign it to both collections without having to save multiple copies of the file.
-
This is a big one — it does the majority of the data entry for you, especially if you are saving items from a library database or Google Scholar. It’s certainly worth double-checking citations for the details of your actual Works Cited or Bibliography, but it’s a great start toward having the info you need when you need it.
But nothing’s perfect, right? A few things I’d like to see improved? I am glad for its vibrant online development community, where considerations are taken seriously. In fact, a few of my concerns have turned out to already be answered, with a little research!
-
Having smoother mobile integration, especially for tablets
-
Plug-in reliability: I’ve had to un-install and reinstall my browser “connector” a few times when it wasn’t recognizing all of the fields for articles, and just thinking they were web pages. Not the end of the world — it’s a quick process, and that “free” open source price tag is more than worth a few hiccups — but it would be great for it to be a bit more consistent.
All in all, Zotero has really made a difference in how I organize ongoing projects. If you have a chaotic folder or two of your own, give it a try! Here’s a great YouTube video explaining how to get started moving over the files you’ve already got.